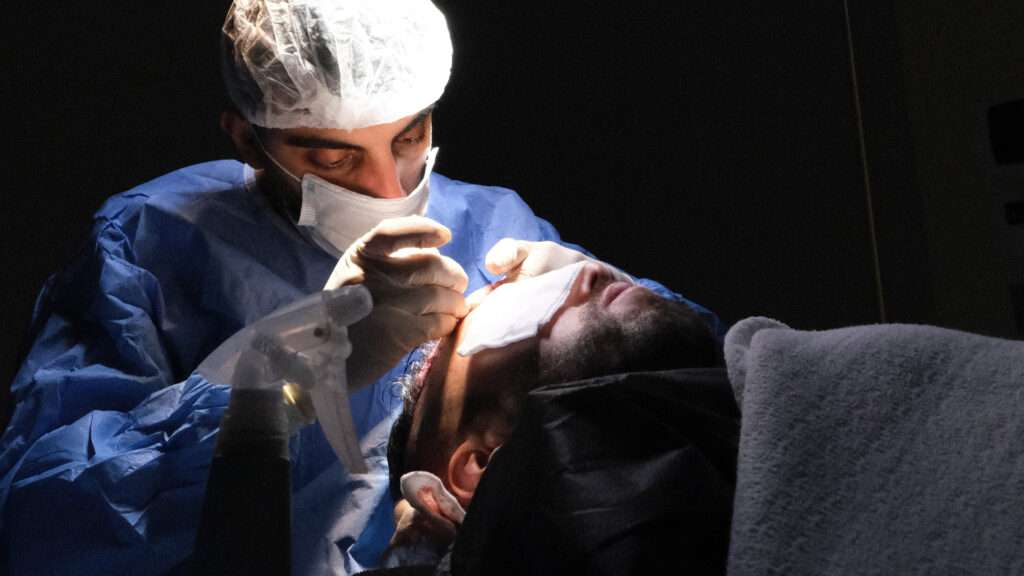
Hair transplant and hair restoration are a particularly popular cosmetic surgery for men, for which Istanbul, Turkey, the world capital of medical tourism, has built an international reputation. Thanks to their experience and the use of the latest techniques available in the field, the hair transplant clinics offer an unbeatable quality/price ratio, with hair transplant costs 60 àto 80% cheaper than in the UK, the Netherlands or in the United States. Among these advanced medical technologies, the robotic hair transplantation procedure has a prominent place. This technique, called IFA (Automatic Follicular Implantation), relies on robots that automatically select and remove the grafts from the donor area in a faster, more efficient and less expensive way, before being transplanted to the recipient area. The first consultation with your hair clinic doctor shall determine the best suited hair transplant technique for your case.
Robotic hair transplant: how does it work?
There are two types of hair transplant robots, which differ in the technology used and in their use. Both use new digital technologies to identify, select and capture the grafts from the donor area and perform micrografts, as the extracted grafts are between 0.8 and 1 mm long. Finally, thanks to the automation of the procedure, 100% of the grafts removed are intact, and can be re-implanted with a chance of regrowth of more than 97%.
On the other hand, some specialists observe that the robotic hair restoration systems can damage neighbouring grafts, which is not the case with a manual hair transplant. In both cases, the donor and recipient areas will be shaved beforehand, and drawn by the practitioner conducting the procedure. Microinjections of anaesthetic are performed on the working areas, making the procedure painless for the patient. These non-invasive systems allow hair transplants to be performed in half the time of a manual procedure. They do not damage the epidermis and leave no scars, making the procedure invisible ten days after the operation.
Currently, the vast majority of hair care clinics equipped with state-of-the-art systems use robots to extract the follicles and then re-implant them manually using the FUE (Follicular Unit Extract) technique and/or DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) technique. To “boost” hair growth, they couple the procedure with a PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma) treatment, which consists of extracting some blood from the patient, passing it through a centrifuge and reinjecting it into the recipient area.
- Neograft SAFER Robot: Neograft was the first company in the world to launch a hair transplant assistance robot in 2009 with the S.A.F.E.R. system, which means “safer” in English. Neograft’s SAFER robot is a compressed air punch (or micro-punch) connected to the system and equipped with a rotating micromotor that will extract and suck out the follicles. To harvest the grafts, the surgeon will take the punch in hand, adjust the speed of the rotary motor according to the nature and quality of the hair, and puncture the grafts one by one, each graft containing between 1 and 5 follicles. They are then removed and placed in a row on sterile pads soaked in saline solution. Once the harvesting is complete, the surgical team will analyse and sort the follicles, then prepare the reimplantation area by injecting an anaesthetic, making micro incisions and finally manually planting the previously harvested follicles, following the FUE and/or DHI procedure.
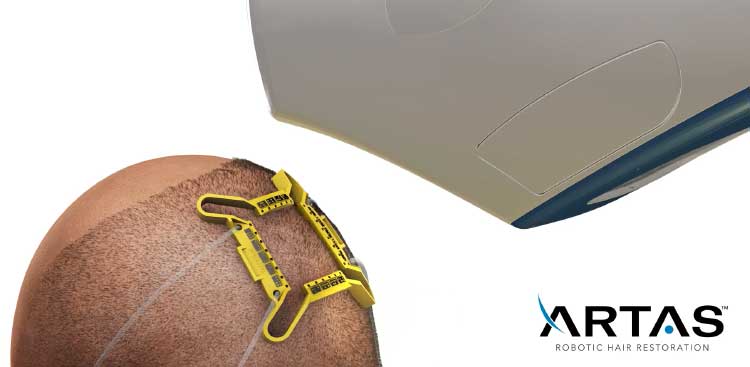
- ARTAS Restoration Robotics: Created by the American company Restoration Robotics in 2008, ARTAS robotic hair transplant system received its marketing approval in 2011. It is now the most widely used robot in the world in the field of hair transplantation. The ARTAS system is a larger machine, equipped with digital cameras and automated punches, which is placed directly on the patient’s scalp. While the cameras transmit a magnified image on a screen, allowing the practitioner to control the operation, the robot uses several algorithms to automatically select and harvest the strongest and most prolific follicles. The grafts are regularly unloaded and made available to the surgical team. Once the grafts have been harvested and carefully preserved in saline, the medical team analyses and sorts the follicles, before manually implanting the follicles extracted by the robotic systems, using the FUE and/or DHI procedure, for a more natural result.
In 2018, Restoration Robotics (the company has since merged with Venus Concept) launched a version of the ARTAS robot that not only harvests, but also reimplants follicles: this makes hair transplantation fully automated and much faster than manual transplantation. This machine is being deployed in some specialised clinics, including in Turkey, and allows more patients to be treated at lower cost. However, the most experienced hair surgeons still prefer FUE and/or DHI transplantation, because of the investment cost, a limited loss in grafted hair follicles, and because of a lack of visibility regarding the long-term results of a fully automated implantation.
Unlike Neograft, which requires dexterity and experience on the part of the surgeon, the ARTAS robot leaves no room for human error and works with extreme precision. It can harvest between 500 and 1000 grafts per hour, allowing the surgeon to focus his or her energy and attention on implanting the extracted follicles in the hairless area.
A surgical team assisted by the ARTAS robot can extract up to 6,000 follicles in a one-day session, especially for completely bald men with complete alopecia. Due to human fatigue (of both the patient and the surgical team), a hair transplant with manual extraction is limited to 3000-3500 grafts per day. However, 90% of hair transplant operations generally require between 2000 and 3500 follicle implants. Some hair surgery specialists believe that beyond 3,500 grafts removed, the extraction can create dermal trauma to the patient’s scalp, thus compromising the regrowth of the donor area.
What are the advantages of robotic hair transplantation?
- The use of algorithms by the robotic grafting system makes it easier to select patients whose hair is best suited to automated extraction, by analysing the nature of the hair, its angle of growth and its density. This identification facilitates the surgeon’s work.
- The speed of robotic extraction reduces the intervention time of a hair transplant by about 50%, and reduces the fatigue of the medical team, which can better focus on the implantation of the grafts extracted by the robot.
- With a shorter procedure time and less sitting time, patient comfort is more assured than with a manual hair transplant.
- With reduced manual intervention, robotic extraction can reduce the price of a hair transplant by about 30%, making the operation more affordable for more patients.
- Non-invasive, non-painful, automated extraction is more precise and reduces trauma to the capillary dermis, and leaves no scars or traces of surgery ten days after the operation. The patient can return to his or her normal life the next day, provided of course that the surgeon’s recommendations for post-operative care are followed.
- The waiting time of the grafts, between extraction from the donor area and implantation on the recipient zone, is reduced, allowing a better chance of regrowth, of the order of 97%.
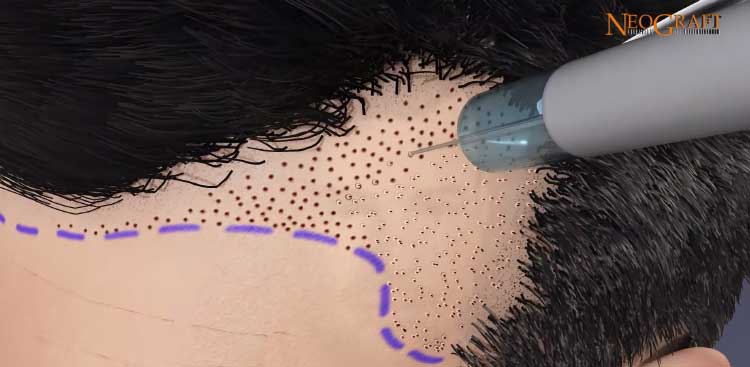
What are the disadvantages of Robotic Hair Transplant?
- Robotic extraction is not suitable for very fine or frizzy hair.
- The ARTAS robot is easily used on the side of the skull or on the occiput, the most common donor area. However, it does not allow grafts to be harvested elsewhere, such as the neck, face or torso, whereas manual extraction can be performed anywhere, especially in the case of a patient suffering from complete alopecia, where grafts will have to be harvested elsewhere than on the skull.
Automated or manual hair transplant: which technique to choose?
Depending on your hair type and the size of the area to be covered, the robotic hair transplant will be more or less suitable. Its use will be determined after the analysis of your hair loss problem and the diagnosis of your specialist surgeon. Currently, many practitioners prefer to mix the different techniques, entrusting the harvesting to the machine if your hair type is adapted and preferring to implant the extracted follicles following the FUE and/or DHI protocol.
IFA is best suited to early and moderate baldness in men and partial or diffuse alopecia in women. It can also be applied to patients wishing to reconstruct eyebrows or hide scars.
What is the difference between FUE, DHI, FUT and IFA?
- FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) is a hair transplant performed by hand. It can be applied either to the whole operation (extraction and implantation) or only to the implantation phase.
- FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) is the oldest hair transplantation technique. It consists of extracting a more or less large strip of scalp (between 10 and 25 cm) from the cranial occiput, then extracting the follicles before replanting them on the hairless area and closing the donor area with sutures or staples. Less and less used by specialists, it has the disadvantage of being more painful, and of leaving a scar on the donor area.
- DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) is a hair transplant performed with a Choi punch pen, which is used by the clinic surgeon to extract and re-implant the follicles almost instantly. This is the least invasive and most precise hair transplantation technique, but also the one requiring great dexterity and experience on the part of the practitioner, and therefore the most expensive.
- The IFA or robotic hair transplant (Automatic Follicular Implantation) is a hair transplant assisted by a robotic system that automatically analyses, selects and sucks up the follicles and then makes them available to the surgical team for manual implantation, using the FUE and/or DHI technique. With technological progress, it will soon be possible to fully automate a hair transplant, as is already the case with the ARTAS 9X robot.

What is the price of a robotic hair transplant?
- Turkey: €1500 to €3500
- UK: £3000 to £8000
- Netherlands : €3000 to €8000
- Switzerland: €4000 to €9000
- United States: $6000 to $12,000
The prices shown here are for a partial or medium hair transplant, including robotic extraction and FUE implantation of approximately 2500 grafts, with PRP treatment.
26498 vues
0 commentaires
1




Il n'y a pas de commentaires pour le moment.