Hair loss and androgenetic alopecia affect millions of people worldwide. Beyond the physical consequences, they can significantly impact self-esteem and confidence. Fortunately, hair transplant techniques have evolved considerably in recent years, offering effective and lasting solutions for regaining a thick, natural head of hair.
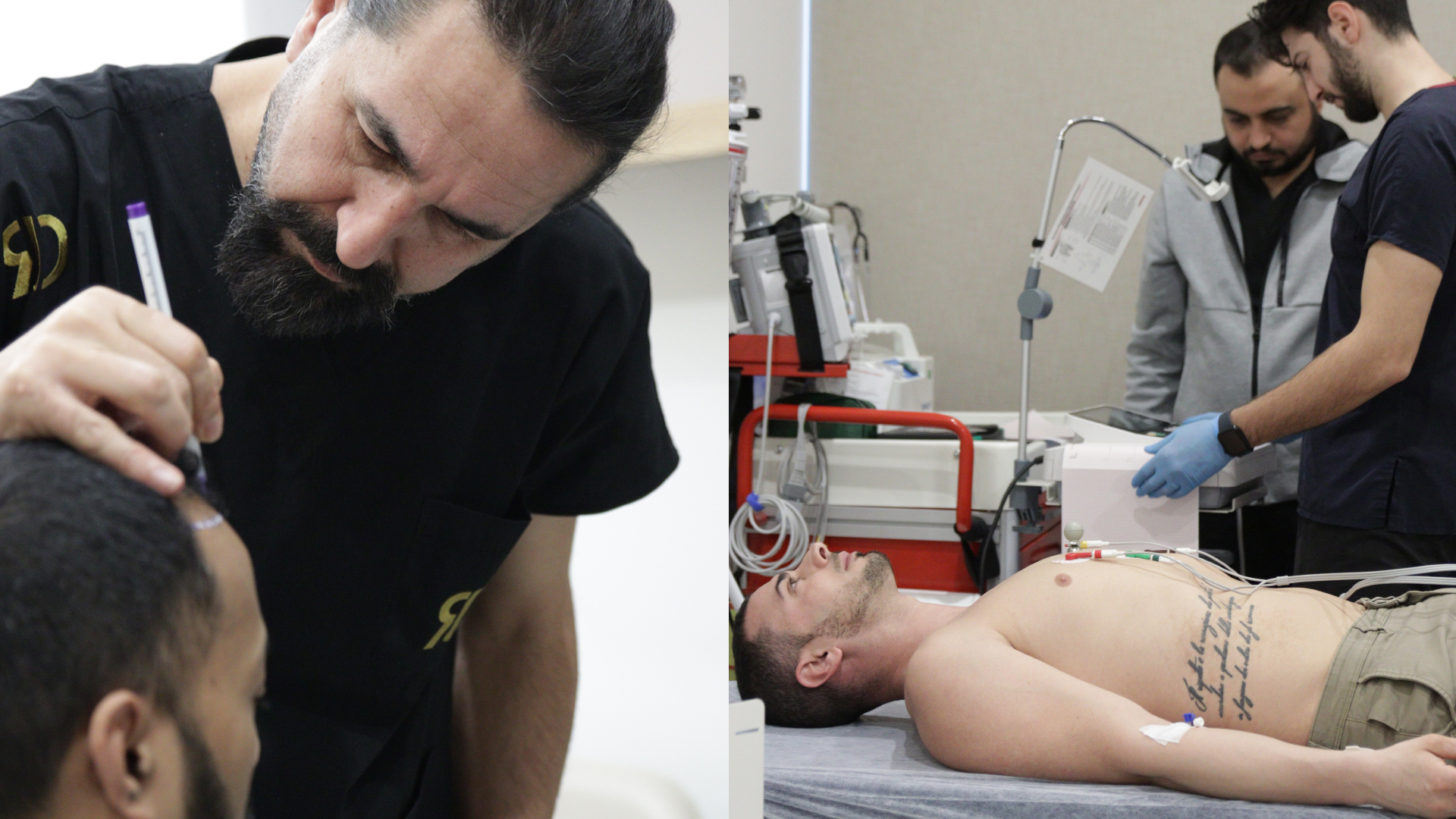
Among today’s most advanced and popular techniques, two methods stand out: FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) and DHI (Direct Hair Implantation). But how do you choose between these two approaches? Which technique is best suited to your specific situation? This article provides a comprehensive and objective comparison of these two methods to help you make an informed choice.
The FUE Technique: Principles and Process
FUE or Follicular Unit Extraction is a modern hair transplant technique that has revolutionised the field of hair restoration. Unlike the older FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) method that required harvesting a strip of scalp, FUE is much less invasive.
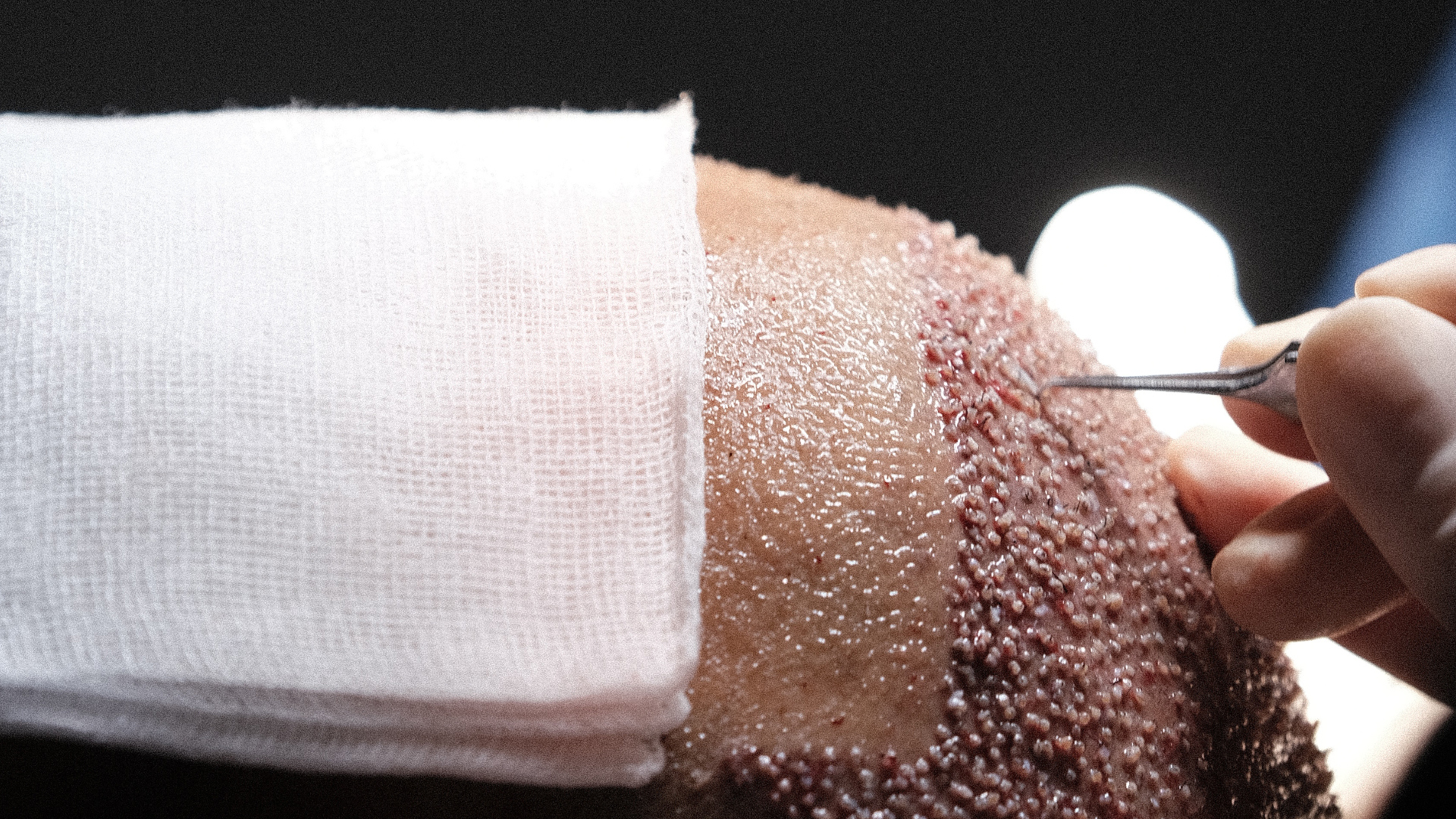
How Does FUE Work?
The fundamental principle of FUE is based on the individual extraction of hair follicles from the donor area, typically located at the back of the head. The surgeon uses a micro-punch (surgical instrument) with a diameter ranging from 0.7 to 1 mm to extract each follicular unit one by one. This meticulous technique avoids visible linear scarring and significantly reduces recovery time.
A standard FUE procedure unfolds in several key stages:
- Preparation of the donor area: Shaving and local anaesthesia
- Graft extraction: Individual harvesting of follicular units
- Graft preservation: Maintenance in a special solution
- Creation of recipient channels: Precise incisions in the treatment area
- Graft implantation: Meticulous placement of follicles
- Post-operative care: Specific instructions to optimise results
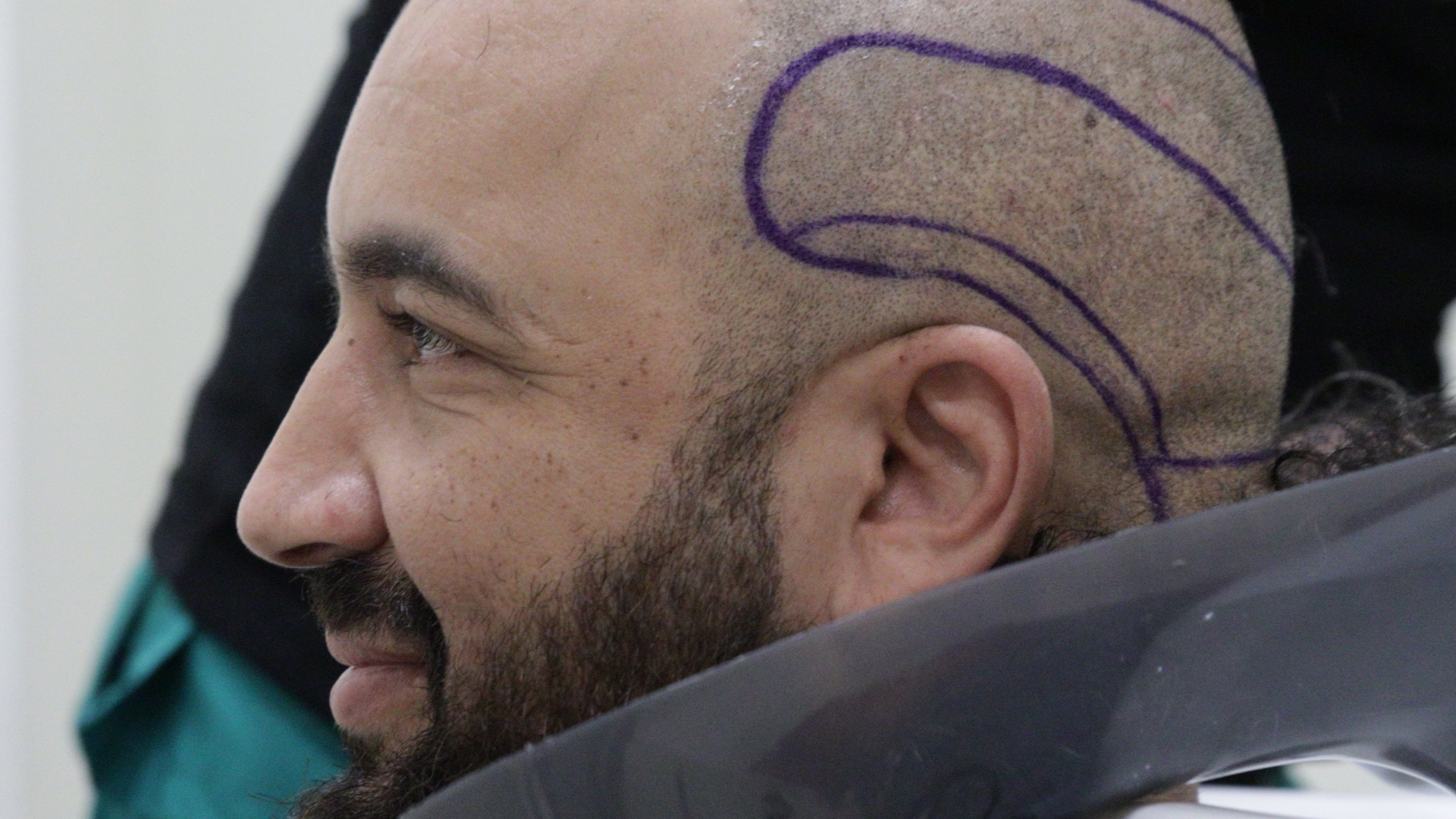
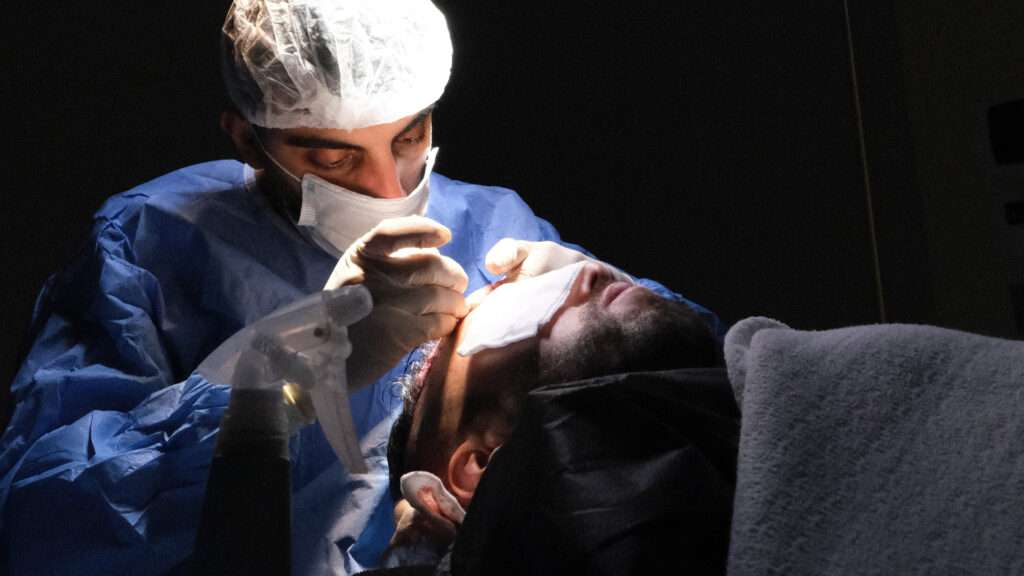
First, the surgeon shaves the donor area to facilitate access to the follicles. Local anaesthesia is then administered to ensure patient comfort during the procedure. The practitioner then extracts individual grafts using the punch. These precious grafts are carefully preserved in a special solution that ensures their viability before implantation.
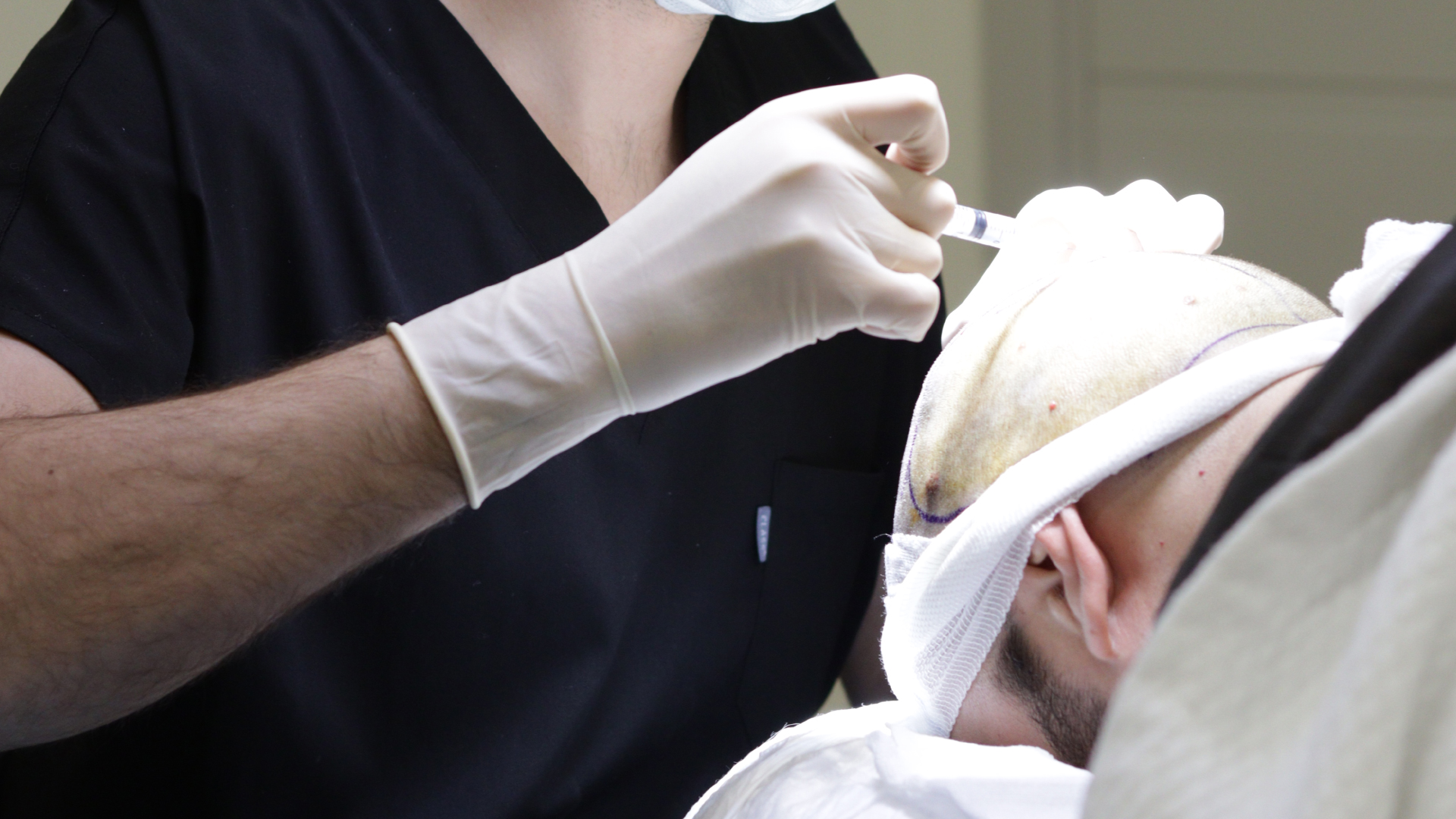
The next step involves creating micro-incisions (recipient channels) in the area to be treated where the grafts will be implanted. Finally, the grafts are meticulously implanted one by one into these previously created channels. The entire process can take between 5 and 8 hours depending on the number of grafts to be transplanted.
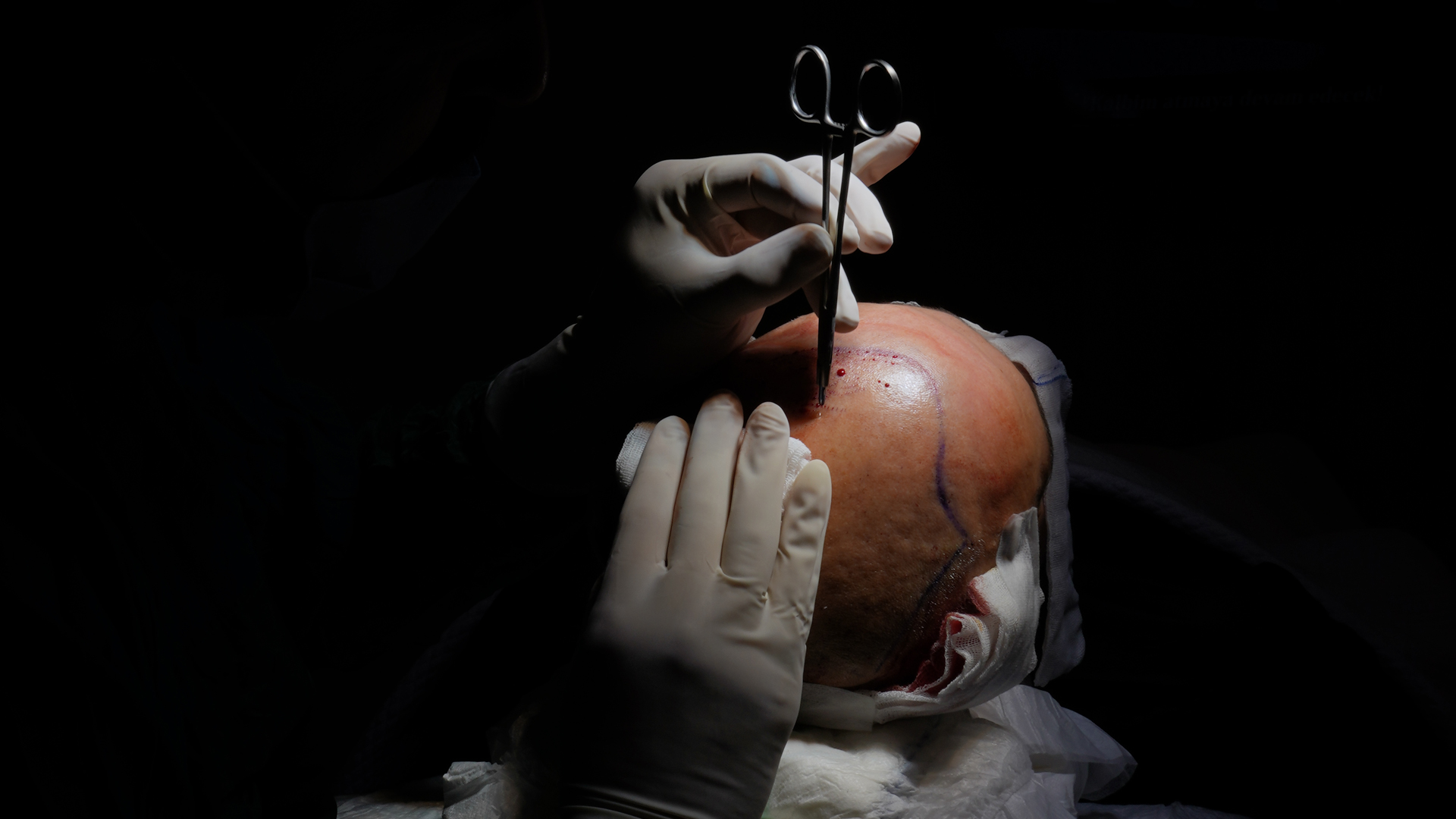
The FUE technique exists in several variants, including manual FUE (extraction performed by hand by the surgeon), motorised FUE (using an electric device to facilitate extraction) and Sapphire FUE which uses sapphire blades to create recipient channels, offering more precise incisions and faster healing.
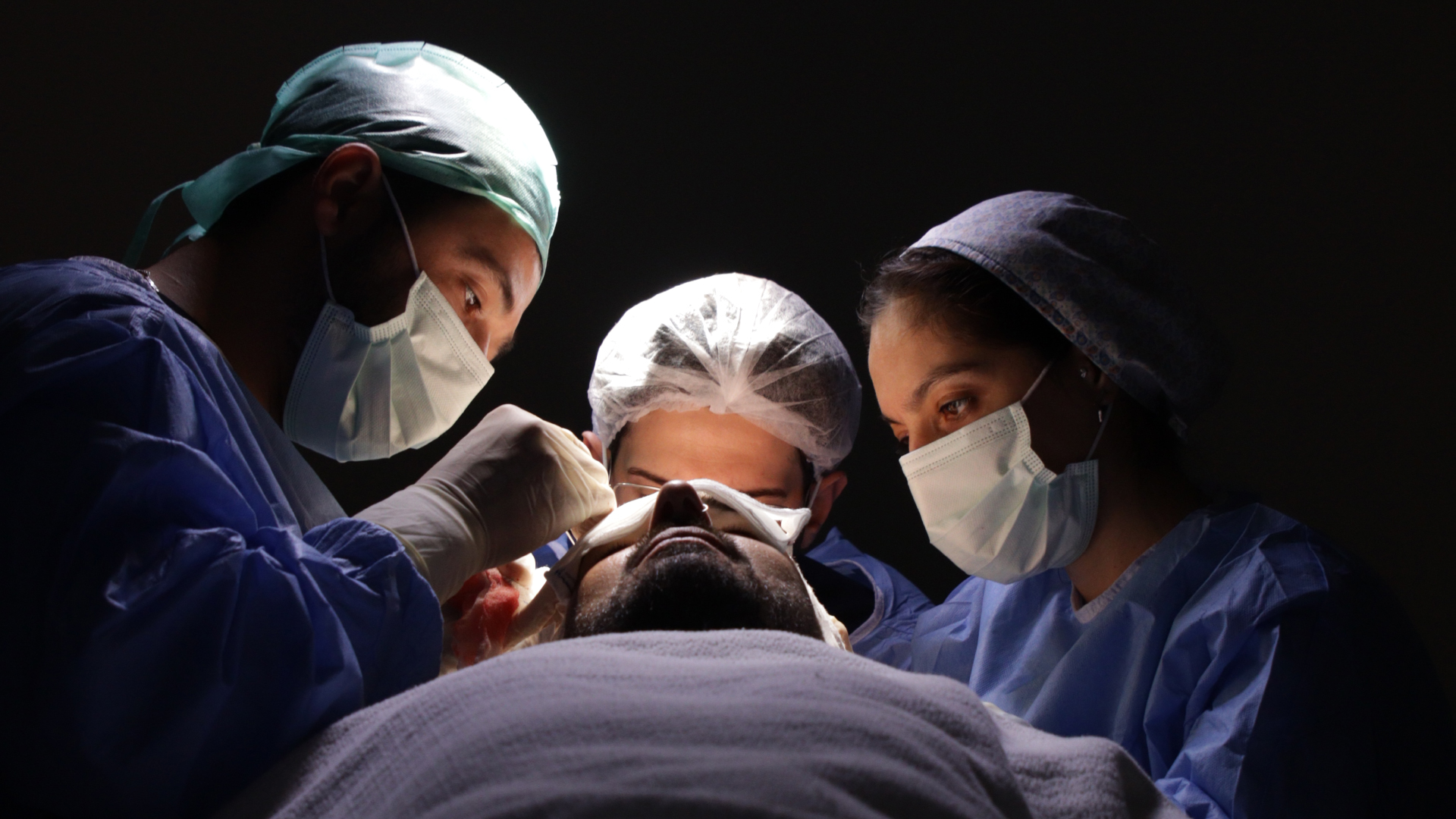
The DHI Technique: The Evolution of FUE
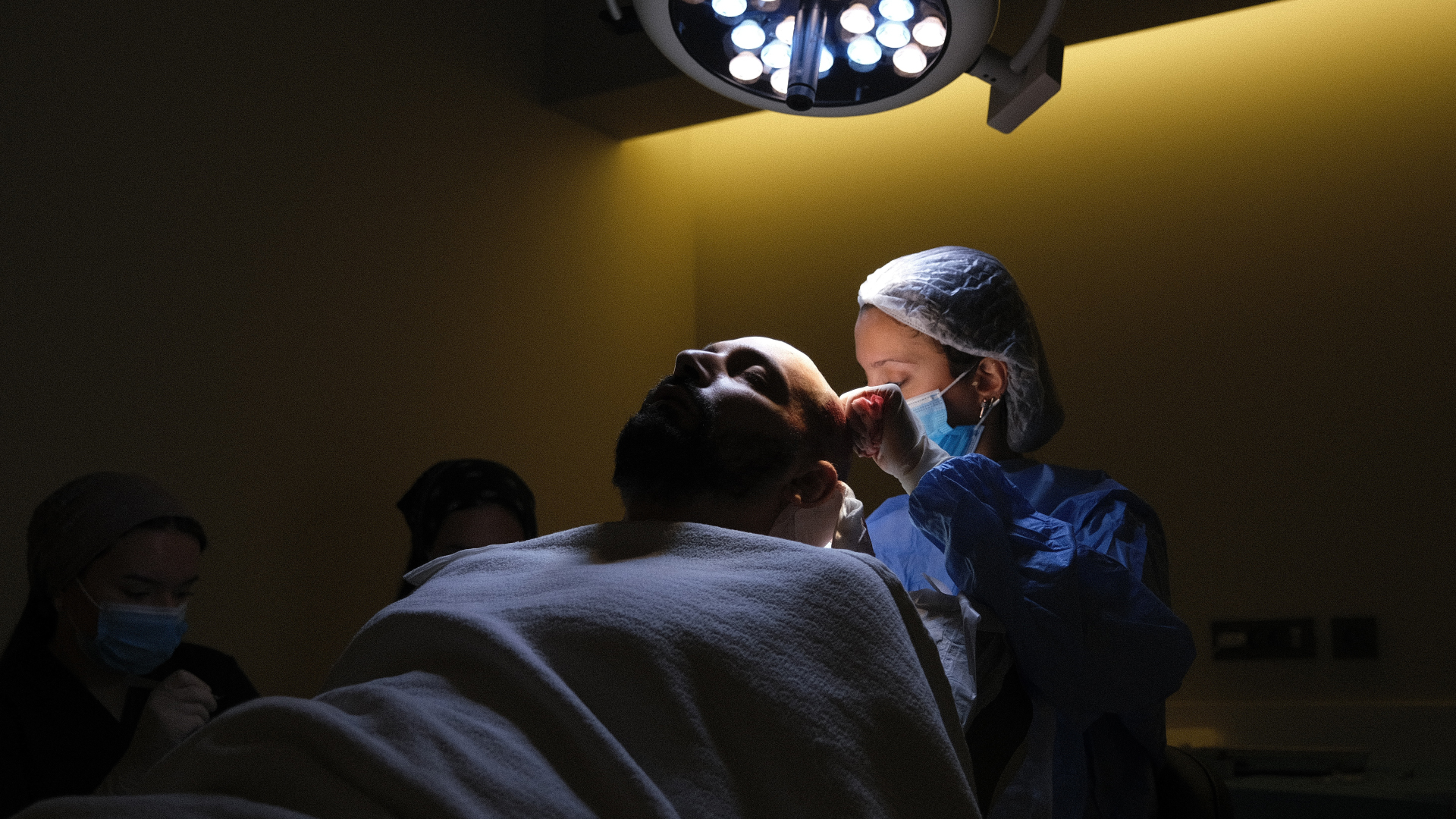
DHI or Direct Hair Implantation represents a significant evolution of the FUE technique. Although these two methods share the same follicle extraction process, they differ considerably in how the grafts are implanted.
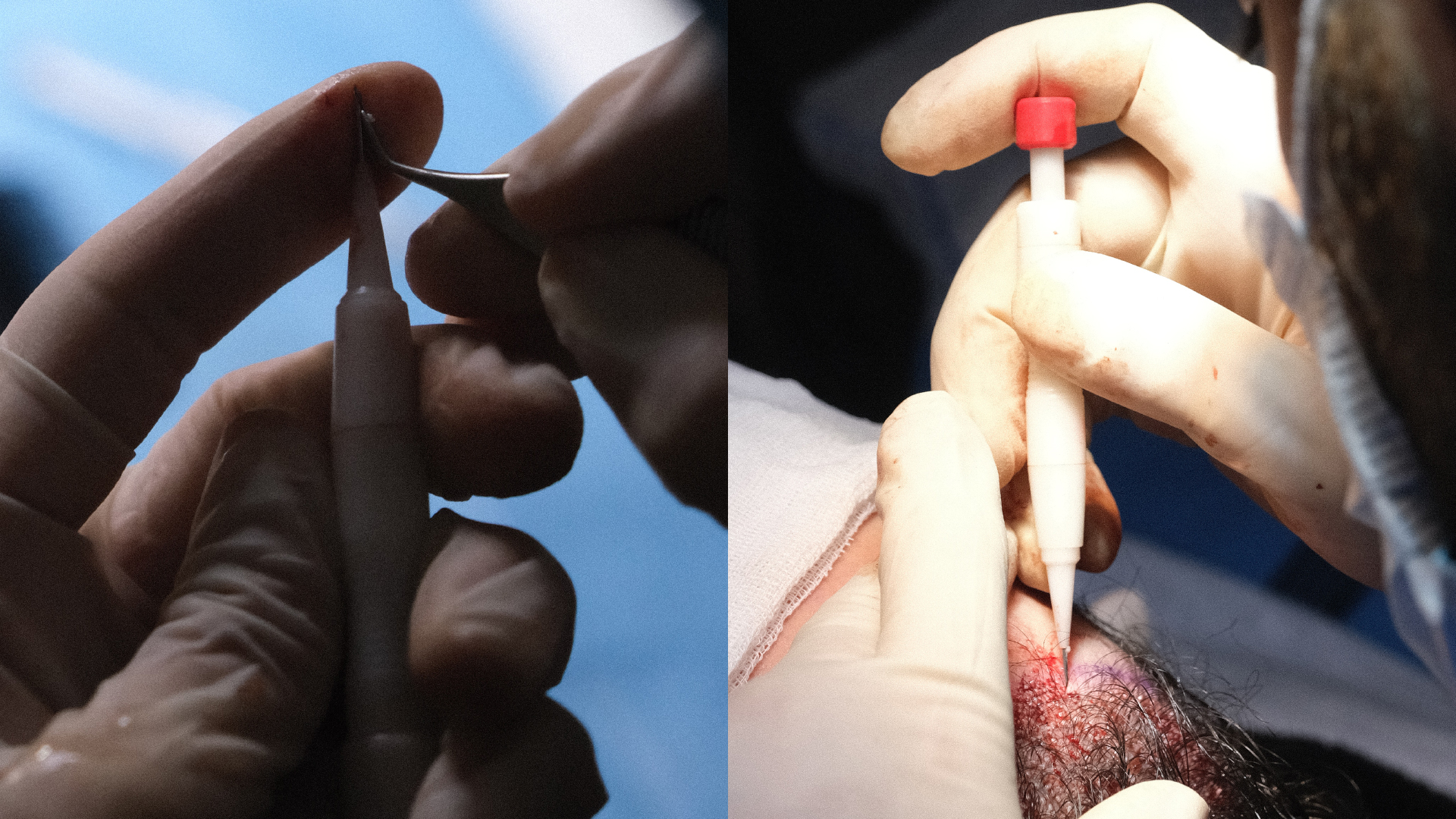
What Does the DHI Technique Involve?
The distinctive feature of DHI lies in the use of a specific tool: the Choi implanter pen. This innovative instrument allows both the creation of the recipient channel and the implantation of the graft in a single action, unlike classic FUE where these two steps are distinct.
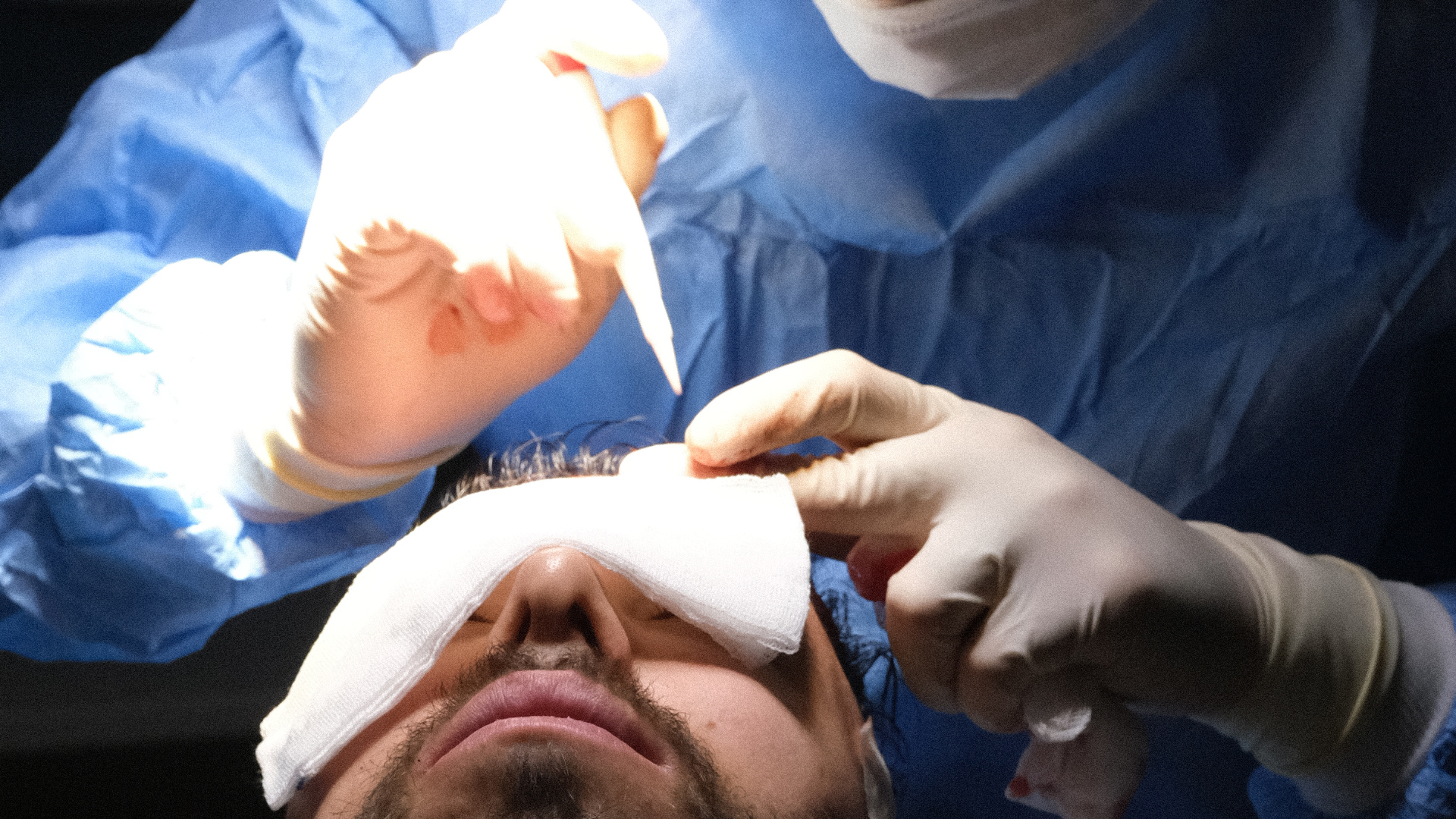
The DHI procedure follows a well-defined process. After partial or complete shaving of the donor area (depending on the case), local anaesthesia is administered. The grafts are then extracted individually, as in the FUE technique. The major difference comes at the next stage: instead of being preserved in a solution while waiting for the recipient channels to be created, the grafts are immediately loaded into the Choi implanter pen.
This special pen allows the surgeon to implant grafts directly into the scalp without prior creation of channels. This approach offers precise control over the angle, depth and direction of each implant, which is crucial for achieving a natural result.
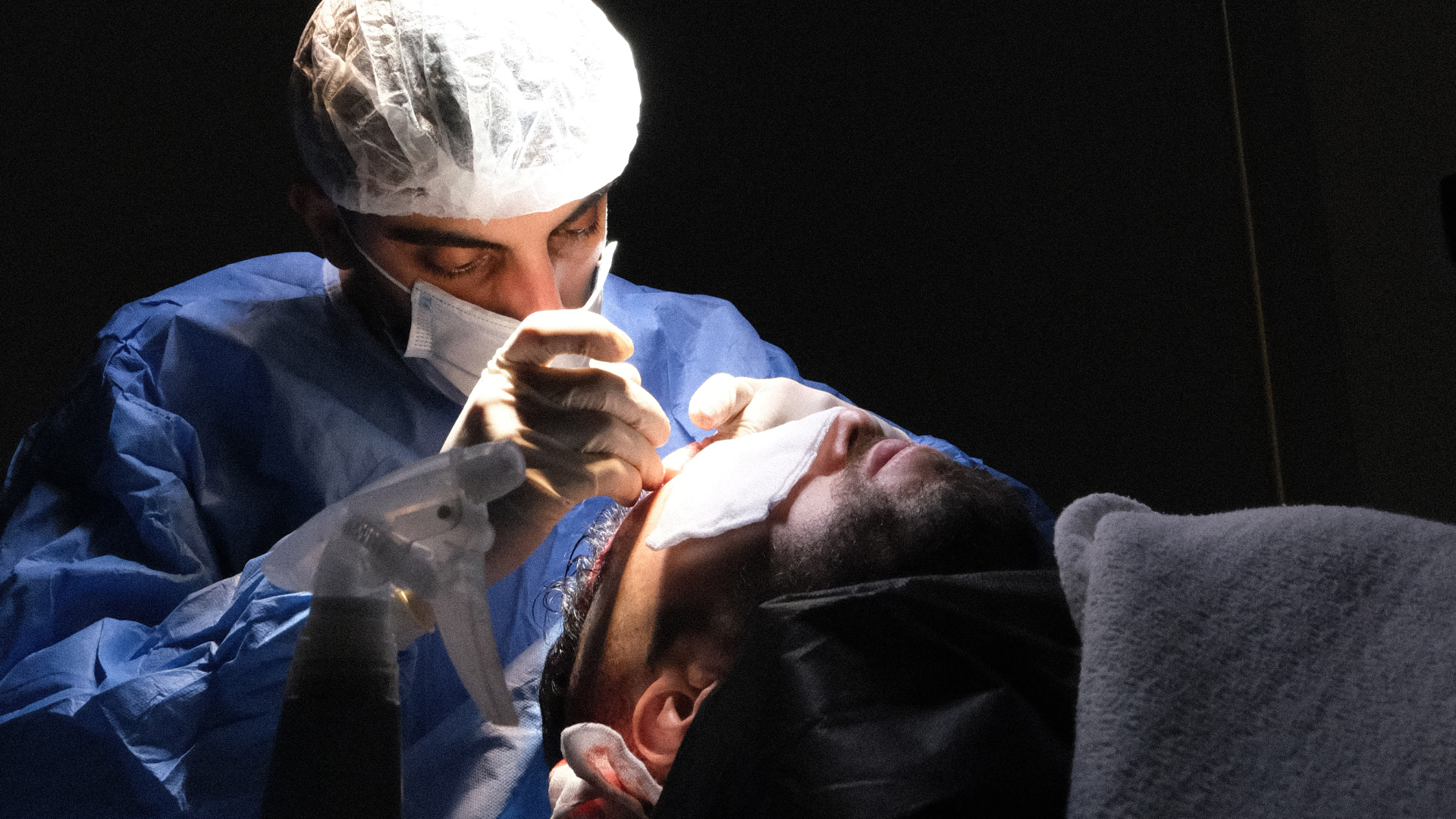
DHI offers specific technical advantages over classic FUE. Firstly, it significantly reduces the time grafts spend outside the body (ischaemia time), which increases their survival rate. It also allows for higher density thanks to the precision of implantation. Finally, DHI offers optimal control over every aspect of implantation, ensuring a more natural result.
Technical Comparison: DHI vs FUE
To understand which technique might be best suited to your situation, let’s examine in detail the differences between these two methods across several key aspects.
The Extraction Process
Regarding graft extraction, DHI and FUE techniques are quite similar. In both cases, follicles are harvested individually using a motorised or manual punch. The graft survival rates during this phase are comparable for both techniques.
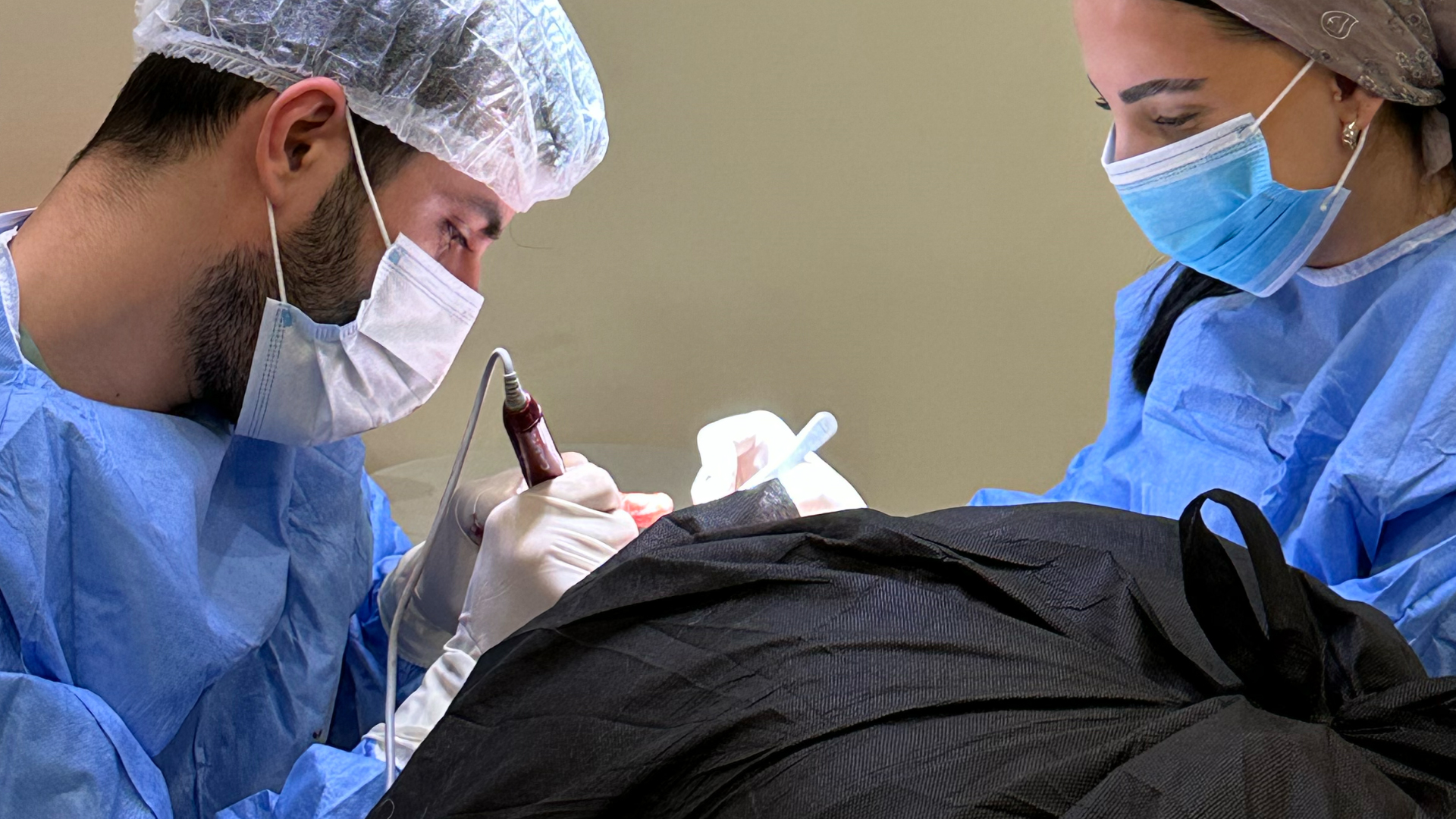
The main difference sometimes lies in graft selection. Some surgeons specialising in DHI pay particular attention to selecting follicular units based on the number of hairs they contain (1, 2, 3 or 4 hairs), in order to implant them strategically for optimal results.
The Implantation Process
It’s at the implantation level that the two techniques diverge significantly. In classic FUE, the surgeon first creates recipient channels in the area to be treated, then implants the grafts into these previously prepared channels. In DHI, these two steps are combined: the Choi implanter pen allows the surgeon to create the channel and implant the graft in a single action.
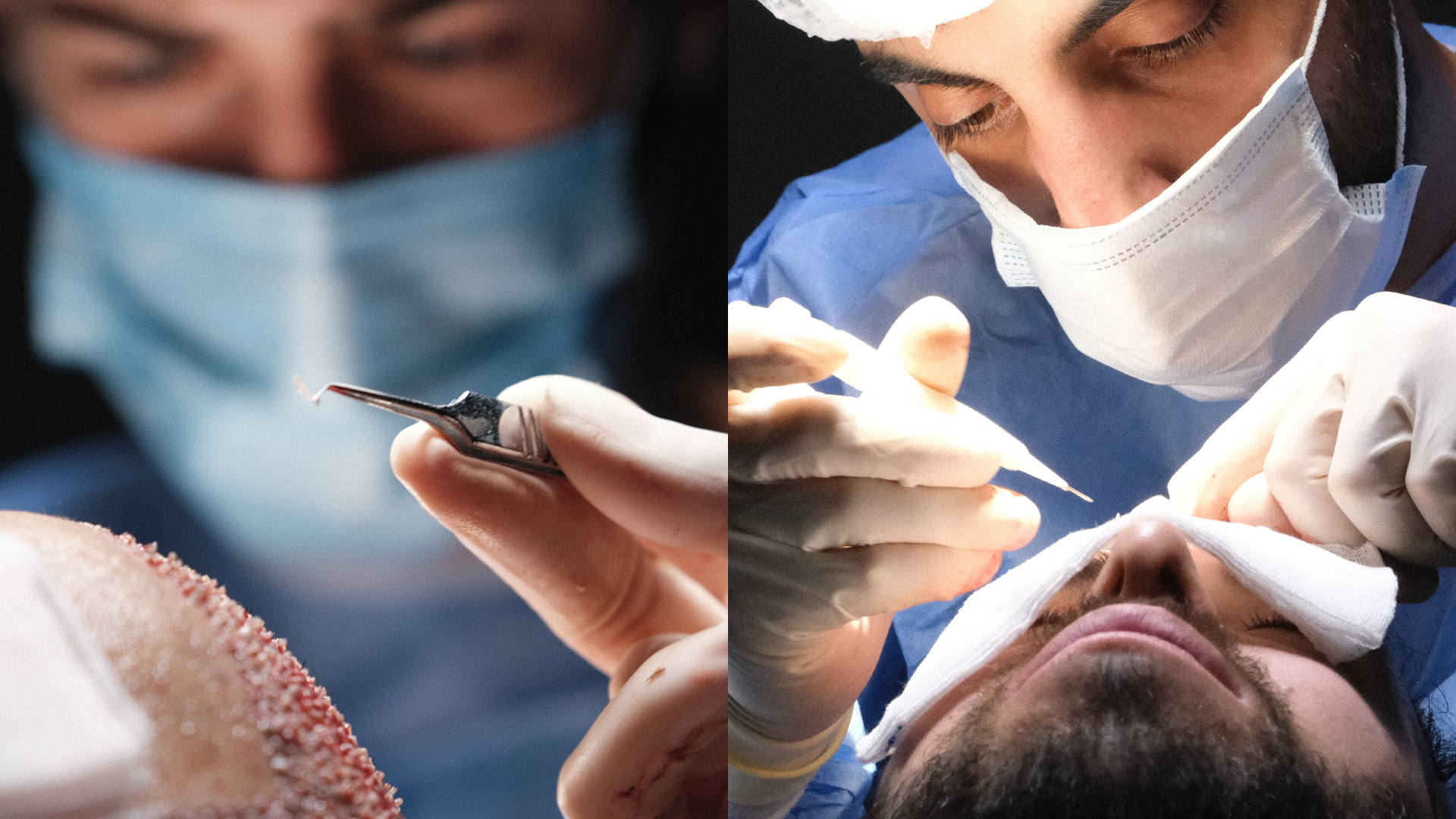
This fundamental difference has several important implications:
- The time grafts spend outside the body is considerably reduced with DHI, which can increase their survival rate.
- The precision of implantation is generally superior with DHI thanks to the finer control offered by the Choi pen.
- The possible density is often higher with DHI as it allows grafts to be placed closer together.
- The risk of graft trauma may be reduced with DHI as they are handled for less time.
Operating Time and Complexity
In terms of procedure duration, DHI generally takes more time than classic FUE for the same number of grafts. This is explained by the increased precision required during implantation with the Choi pen. A DHI procedure for 2000-3000 grafts can take up to 6-8 hours, compared to 4-6 hours for an equivalent classic FUE.
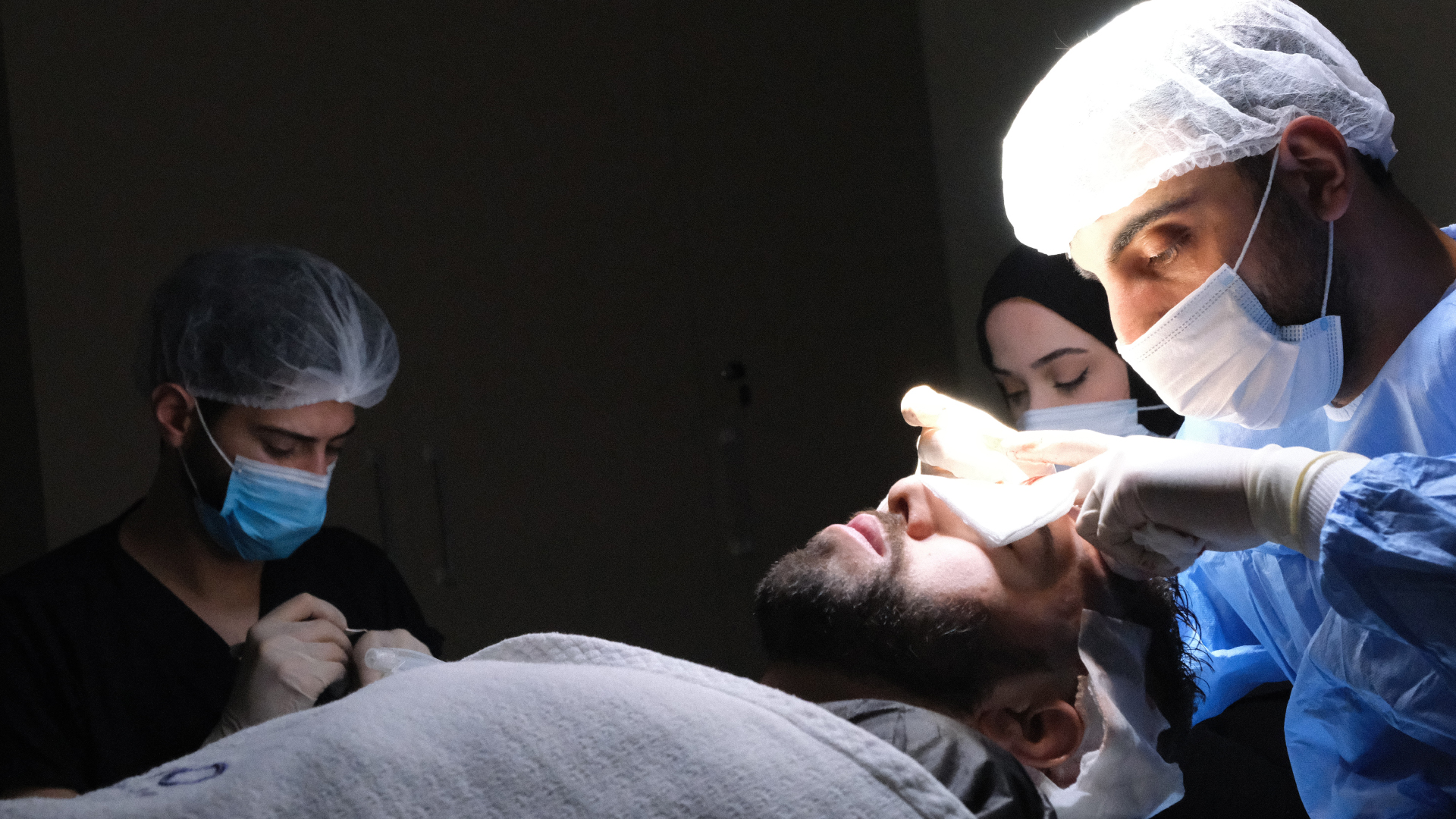
DHI also presents a longer learning curve for surgeons. Mastering the Choi implanter pen requires considerable dexterity and experience. Therefore, it is crucial to choose an experienced surgeon for this technique.
Regarding the medical team, DHI often requires a larger and more specialised team, which can contribute to its higher cost.
Technology and Equipment
The tools used constitute another notable difference between these two techniques. FUE generally employs punches for extraction and micro-blades for creating recipient channels. These micro-blades can be metal or sapphire, with the latter option offering more precise incisions and faster healing.
DHI, meanwhile, uses the Choi implanter pen as its main tool, which constitutes its principal technological differentiator. This instrument allows direct and precise implantation, but requires specific expertise to be used effectively.
Which Patient for Which Technique?
The choice between DHI and FUE depends on several personal factors that should be considered with the help of a specialist.
When to Choose FUE?
FUE may be particularly indicated in the following cases:
- Extensive baldness requiring a large number of grafts (more than 3000)
- Limited budget while seeking satisfactory results
- Large areas to treat as in advanced stages of alopecia
- Moderate density desired rather than maximum density
- Time constraints requiring a faster procedure
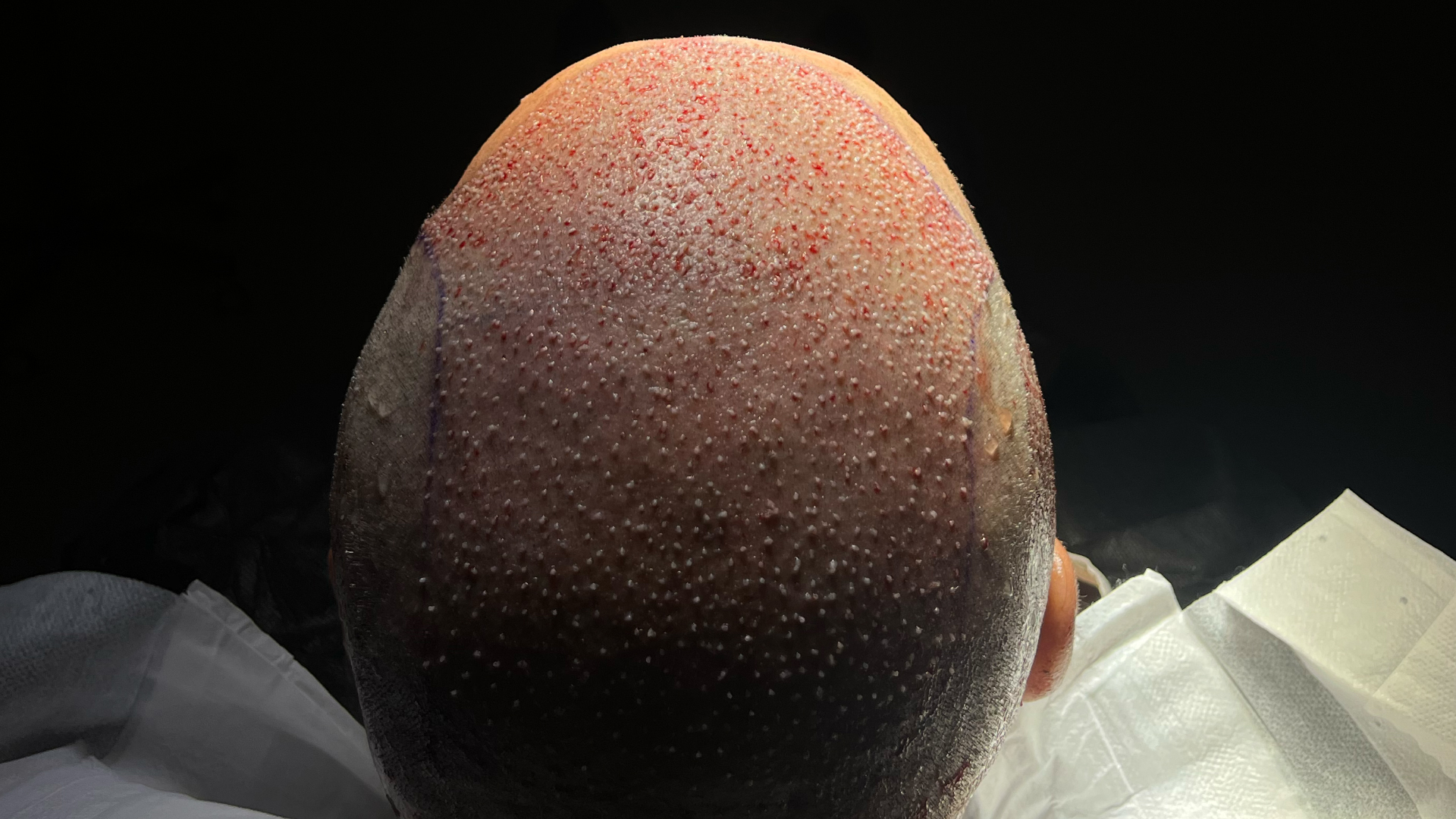
FUE is often recommended for patients requiring a large number of grafts, as it generally allows more follicles to be treated in a single session than DHI. It is also suitable for extensive bald areas, such as advanced stages of androgenetic alopecia.
For patients with a more limited budget, FUE generally represents a more economical option while still offering excellent results. If maximum density is not the absolute priority and a natural but less dense result is acceptable, FUE constitutes an excellent choice. Finally, in cases where speed of procedure is important to the patient, FUE may be preferable as it generally takes less time than DHI.
When to Choose DHI?
DHI can be particularly advantageous in the following situations:
Patients seeking maximum density will find in DHI an ideal solution, as it generally allows for denser implantation. For frontal areas or those requiring particular precision, such as the hairline that defines facial appearance, DHI offers superior control.
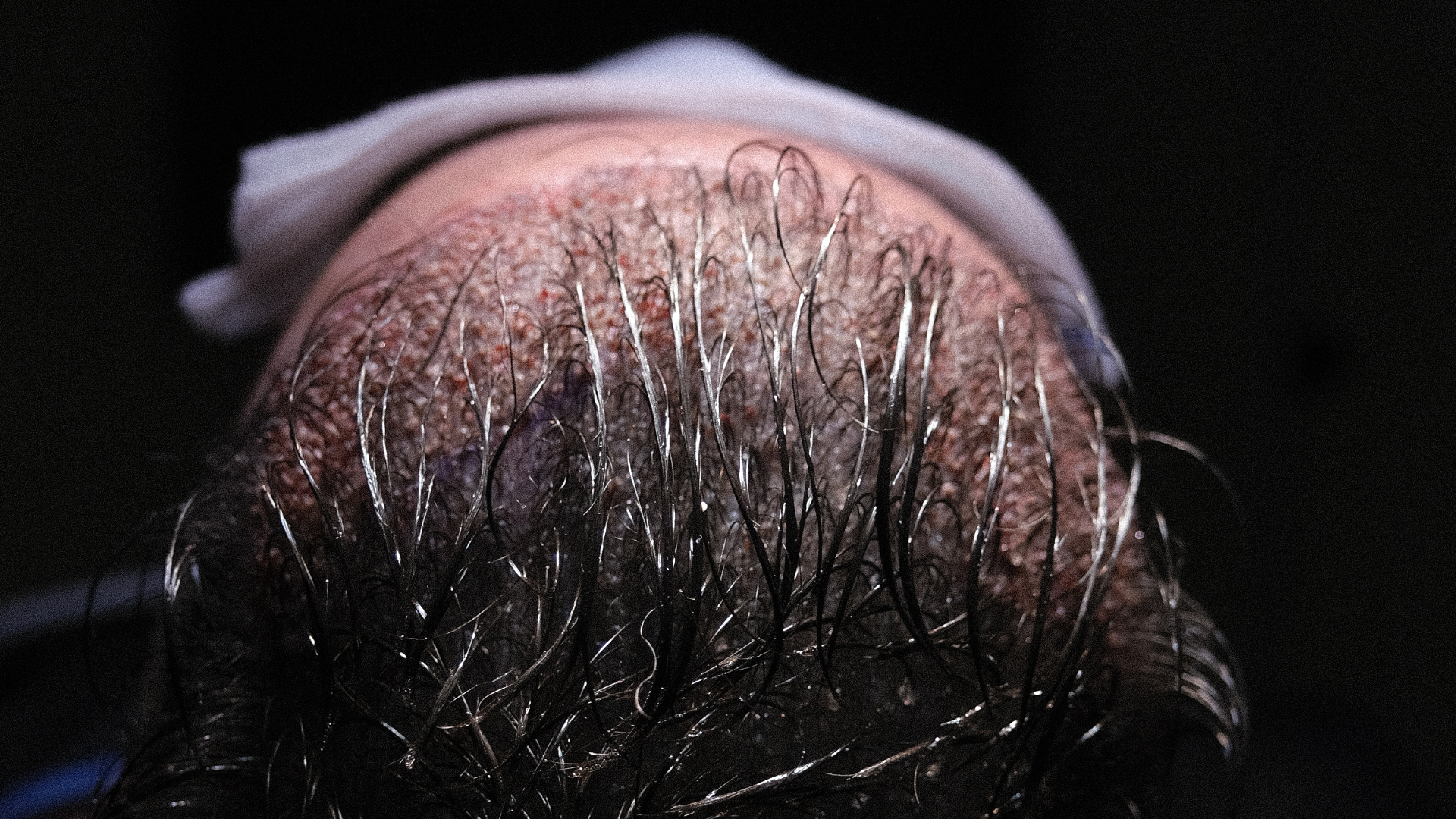
People with fine hair or delicate areas to treat will benefit from the increased precision of DHI. If recovery time is a crucial factor, DHI may be preferable as it generally leads to less oedema and faster healing. Finally, this technique is suitable for people who can afford a higher cost to benefit from the specific advantages it offers.
Contraindications and Limitations
Certain situations may make one technique or the other less suitable. For example, FUE may be less recommended for people with very curly or frizzy hair, as extraction can be more difficult. DHI, meanwhile, may be limited in terms of the number of grafts that can be implanted in a single session, which may require multiple procedures for cases of extensive baldness.
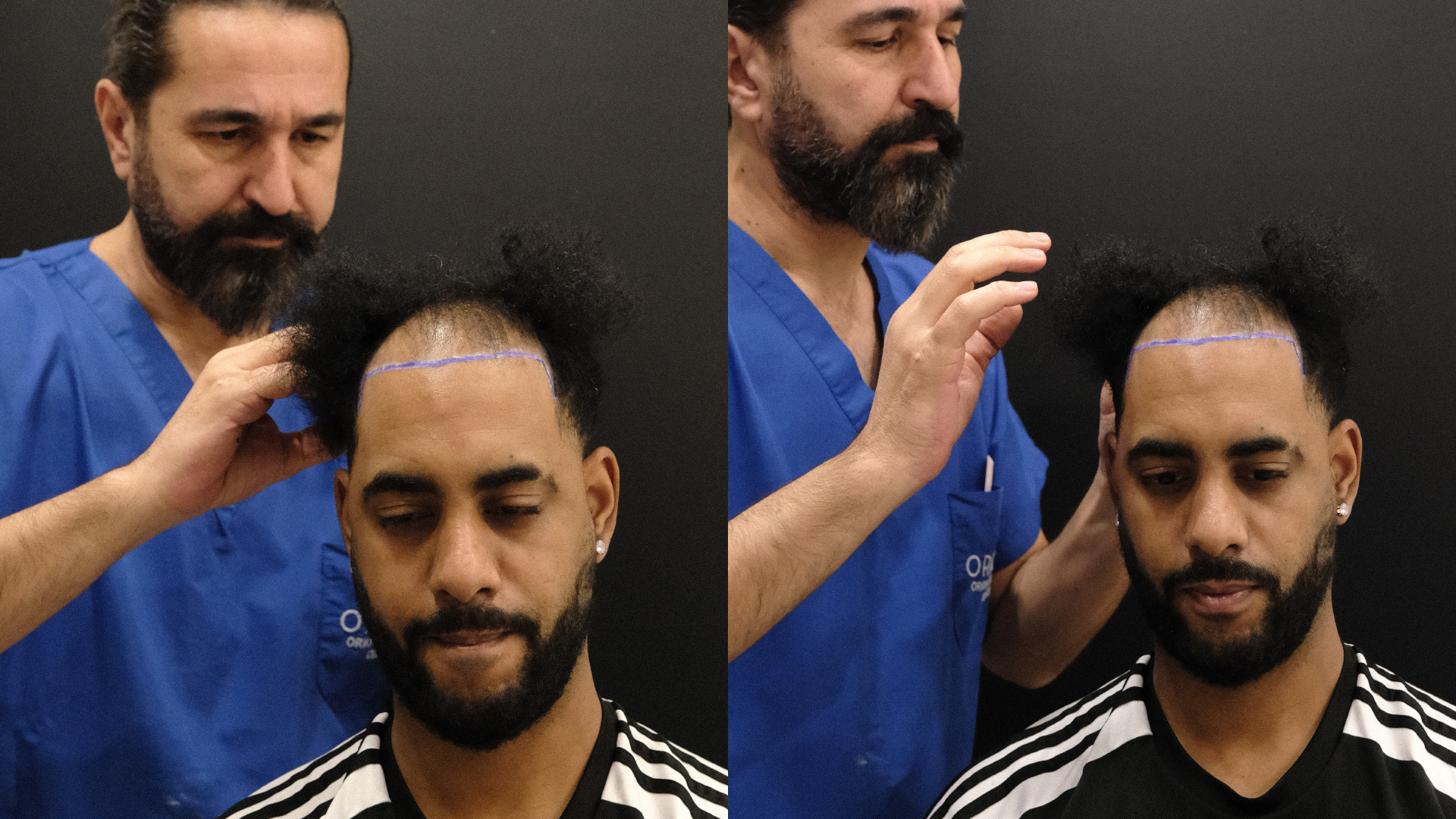
The quality of the donor area is also a determining factor: if it is limited, the surgeon will need to optimise the use of available grafts, which may influence the choice of technique.
Results and Recovery After DHI or FUE Transplant
After the procedure, what can you expect in terms of results and recovery?
Comparison of Aesthetic Results
In terms of natural-looking results, both techniques can offer very natural outcomes when performed by experienced surgeons. DHI may sometimes offer an advantage in terms of density, thanks to the possibility of implanting grafts closer together.
The final quality of results also depends on the graft survival rate. In this area, DHI may present a slight advantage due to the reduced ischaemia time of grafts. However, with good graft preservation technique, FUE can also achieve excellent survival rates.
Comparative Recovery Times
Recovery time after a hair transplant varies according to the technique used. DHI is generally associated with a slightly faster recovery, with less post-operative oedema and faster healing of micro-incisions.
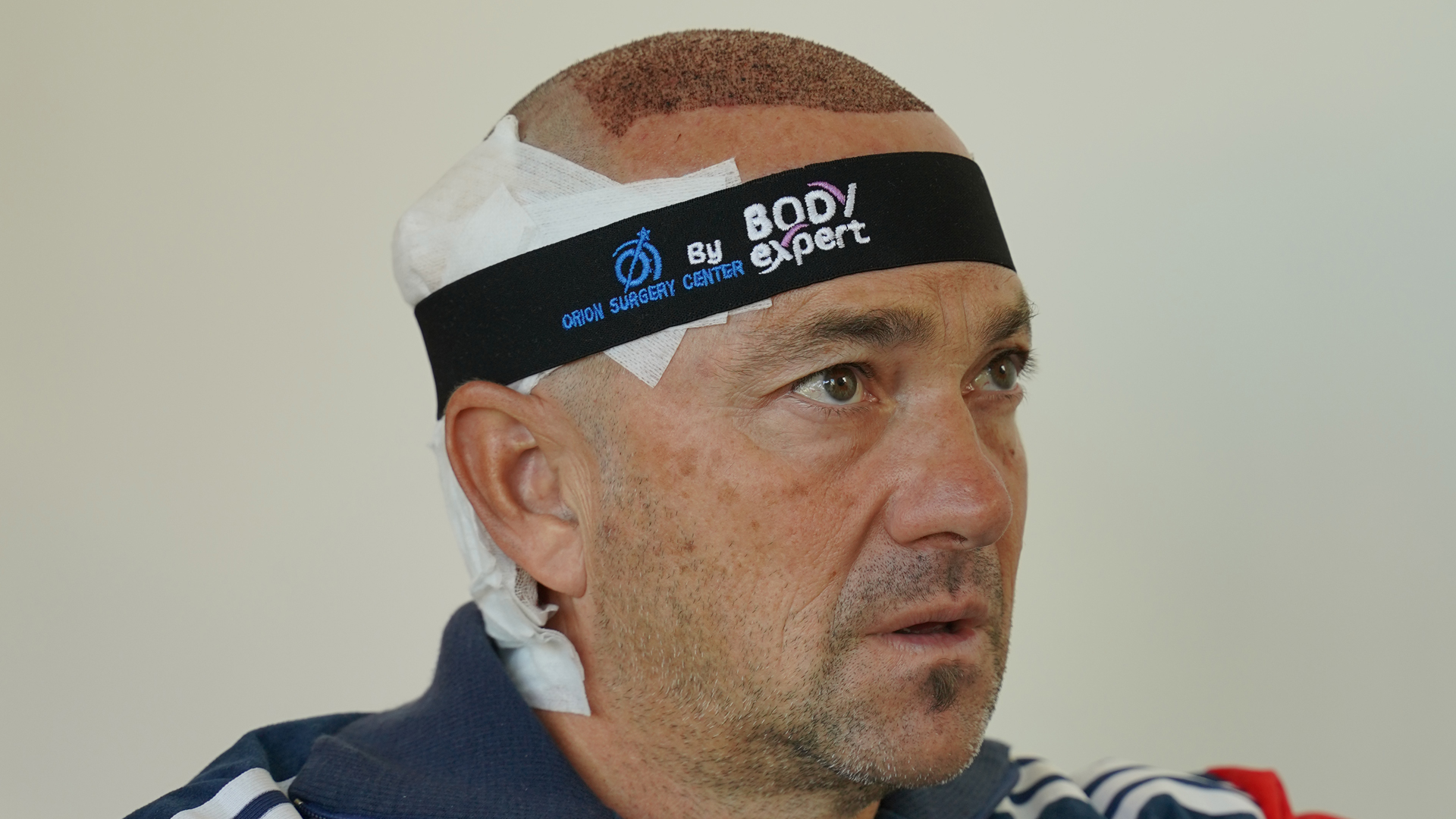

In both cases, patients can expect an initial healing phase of about 10-14 days, during which scabs form around the implanted grafts. These scabs fall off naturally, giving way to the transplanted hair. DHI may sometimes allow a quicker return to normal activities, including professional ones, which can be a significant advantage for some patients.
Regrowth Timeline
Regardless of the technique chosen, the timeline for transplanted hair regrowth generally follows the same pattern:
At 1-3 weeks after the procedure, the transplanted hairs temporarily fall out, a phenomenon called “shock loss”. This is a normal and expected reaction. Between 3 and 4 months after the transplant, the first signs of new growth begin to appear. These new hairs are initially fine and gradually become thicker.
At 6-9 months, results become truly visible, with a significant improvement in density and overall appearance. Between 12 and 18 months, final results are achieved, with mature, natural hairs that can be styled, cut and treated like your original natural hair.
Financial Considerations: DHI vs FUE
Cost is often a determining factor in choosing a hair transplant technique.
Cost Comparison
DHI is generally more expensive than FUE, mainly due to its technical complexity, longer procedure time and the need for a more specialised team. In France, a DHI transplant can cost between €5000 and €8000, while an FUE generally ranges between €3000 and €6000 for a comparable number of grafts.
In Turkey, a popular destination for medical hair tourism, prices are considerably lower: DHI can cost between €2000 and €3500, and FUE between €1500 and €2500. These price differences are mainly explained by the lower cost of living and overhead costs in this country.
The total cost also depends on the number of grafts needed: the larger the area to be treated, the higher the number of grafts will be, and therefore the higher the cost.
Value for Money
The question many ask is whether the additional cost of DHI is justified. The answer depends on your specific situation and priorities. If you are looking for maximum density and faster recovery, the additional investment for DHI may be justified. On the other hand, if your budget is limited and you need a large number of grafts, FUE may offer better value for money.
It is crucial to not choose solely based on price. A very low-priced hair transplant may signal compromises on quality of care, surgeon expertise, or sanitary conditions. These initial savings can lead to much higher costs in the long term if correction is needed.
Body Expert: Premium Support for Your Hair Transplant
Choosing between DHI and FUE is only part of the process. It is equally important to select competent professionals who will support you throughout your hair transplant journey.
Body Expert has established itself as a reference agency specialising in supporting patients for hair transplant procedures in Turkey. Founded by Burak Engineri, himself a former hair transplant patient, the agency benefits from a unique understanding of patients’ concerns and expectations.
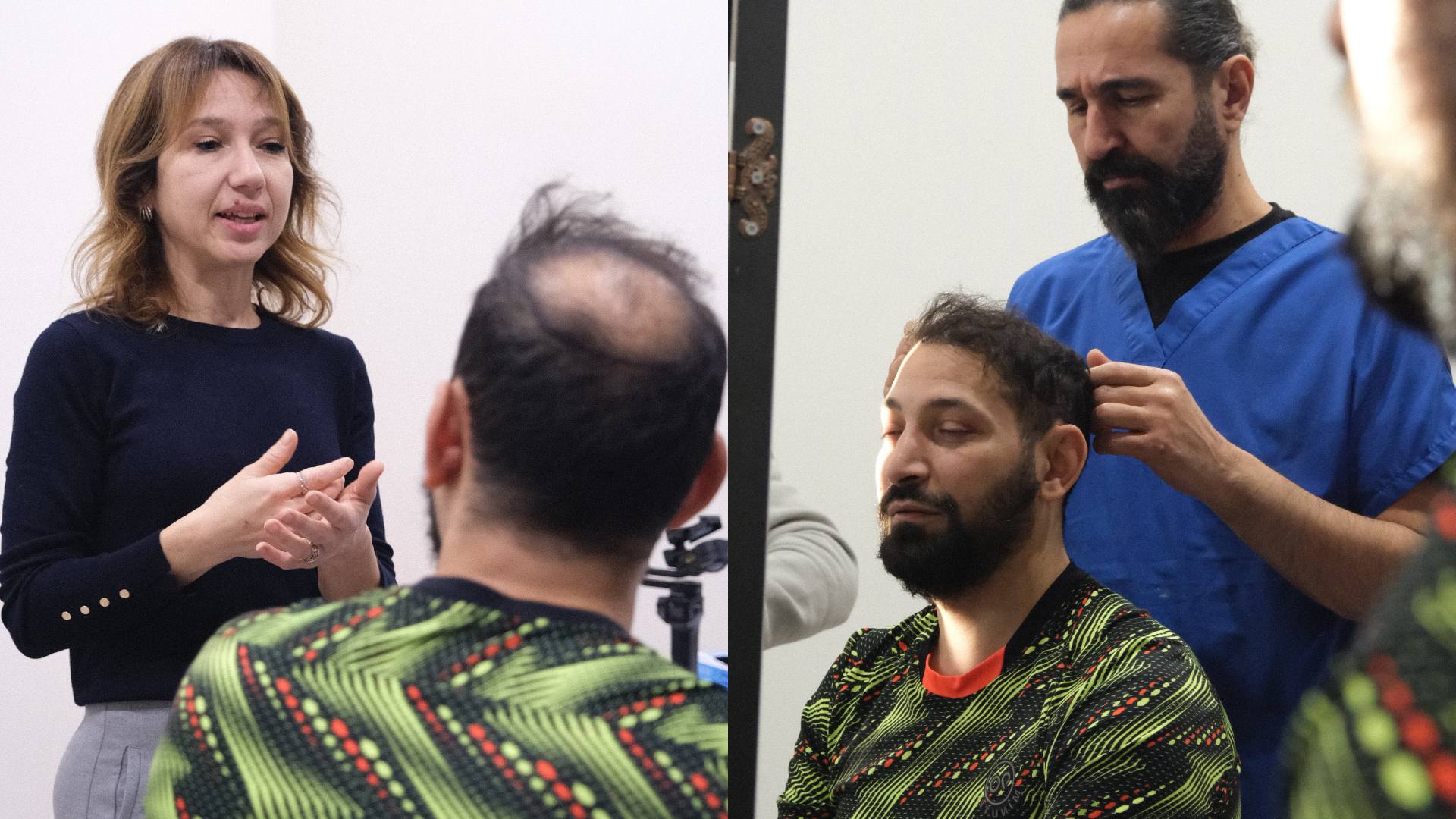

Body Expert’s story is particularly inspiring: after undergoing his own hair transformation, Burak decided to put his personal experience and twenty years of expertise in tourism at the service of others suffering from baldness. This lived experience gives the agency an empathetic and authentic approach that distinguishes it in the medical tourism sector.
The agency stands out for its expertise in both techniques (FUE and DHI) and for its rigorous selection of partner surgeons. Each surgeon is evaluated according to strict criteria of competence, experience and results, thus guaranteeing patients the best possible care.
One of Body Expert’s major assets is its personalised support in French throughout the journey. From the preliminary consultation to post-operative follow-up, patients benefit from a dedicated contact who guides them at each step. This linguistic and human support is particularly reassuring for international patients.
The economic advantages of a transplant in Turkey with Body Expert are considerable, with savings of up to 50 to 80% compared to prices in France or Switzerland, without compromising on quality. The packages offered include comprehensive services: airport transfers, accommodation in quality hotels, presence of an interpreter and thorough medical follow-up.
Many patients testify to the quality of this support: “From the first contact, I was accompanied by a single point of contact, from the beginning to the post-operative follow-up. Even after my return, Body Expert continued to ensure follow-up to make sure everything was going well”, confides a satisfied patient.
Conclusion: DHI or FUE, Which Technique Is Right for You?
At the end of this comparative analysis, it is clear that DHI and FUE are two excellent techniques, each with their specific advantages.
- FUE stands out for its versatility, its ability to treat large areas of baldness and its generally more affordable cost. It remains a reference in the field of hair transplantation and offers excellent results when performed by experienced surgeons.
- DHI, a technical evolution of FUE, offers specific advantages in terms of implantation precision, possible density and recovery time. Its higher cost may be justified for patients seeking these particular benefits.
There is no “best” technique in absolute terms, but a technique better suited to each patient depending on their specific situation. A thorough consultation with a specialist is essential to determine which approach best suits your particular case.
In some cases, surgeons may even recommend a combined approach, using DHI for the hairline (where precision is crucial) and FUE for the rest of the scalp, thus maximising the advantages of both techniques.
The essential thing is to choose competent and experienced professionals, like those selected by Body Expert, who can guide you towards the solution most suited to your situation and support you throughout your hair restoration journey.
Whichever technique you choose, a well-performed hair transplant can transform not only your appearance, but also your self-confidence and quality of life.
Sources
Harris, J. A. (2006). New methodology and instrumentation for follicular unit extraction: Lower follicle transection rates and expanded patient candidacy. Dermatologic Surgery, 32(1), 56-61. https://doi.org/10.1111/1524-4725.2006.32006
Limmer, R. (1996). Micrograft survival. In D. Stough & R. Haber (Eds.), Hair Replacement (pp. 147-149). Mosby.
Parsley, W. M., & Perez-Meza, D. (2010). Review of factors affecting the growth and survival of follicular grafts. Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery, 3(2), 69-75. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-2077.69014
Rassman, W. R., Bernstein, R. M., McClellan, R., Jones, R., Worton, E., & Uyttendaele, H. (2002). Follicular unit extraction: Minimally invasive surgery for hair transplantation. Dermatologic Surgery, 28(8), 720-728. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01320.x
Rose, P. T. (2011). The latest innovations in hair transplantation. Facial Plastic Surgery, 27(4), 366-377. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1283055
Sethi, P., & Bansal, A. (2013). Direct hair transplantation: A modified follicular unit extraction technique. Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery, 6(2), 100-105. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-2077.112672
11085 vues
0 commentaires
0



Il n'y a pas de commentaires pour le moment.